Rio Blanco
Large Instrumented river drains the majority of the south side of the Luquillo Mountains, underline with a granodirite bedrock. Sandy river bed with large boulders. Instrumentation includes multiple gagued streams, lysimeter fields, climate stations, water chemistry sampling as well as other event based and field campaign sampling.
3.26338502 km2 Area
3080 mm Precip
Parent Field Area:
Northeastern Puerto Rico and the Luquillo Mountains ▲
Lithology
meta-igneous
Soil Order
Inceptisol
Biome
rainforest
Land Use
forest land, urban or built-up land
Areas within Rio Blanco
-
Setting & Research
This large instrumented river drains the majority of the south side of the Luquillo Mountains, underline with a granodirite bedrock. Sandy river bed with large boulders. Instrumentation includes multiple gagued streams, lysimeter fields, climate stations, water chemistry sampling as well as other event based and field campaign sampling.
-
Overview Maps
Overview site map.
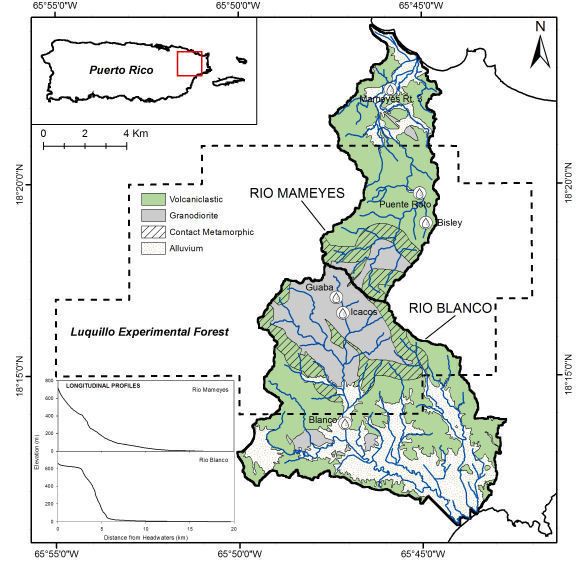
See full size (in new tab/window)
-
Dynamic Map
To fully zoom into a small area, you may need to visit the "Map" button and uncheck "Terrain" view.
-
Data
Icacos/Blanco watersheds - Groundwater Chemistry, Groundwater Depth (2014-2016)
7 components • Rio Blanco • Hydrology, Water Chemistry • McDowell, William H.; Brereton, RichNational - Climate, Flux Tower, Streamflow / Discharge - CUAHSI WDC web services (1968-2015)
7 components • Boulder Creek Watershed, Christina River Basin, Jemez River Basin, Santa Catalina Mountains, El Verde Field Station, Northeastern Puerto Rico and the Luquillo Mountains, Rio Blanco, Rio Mameyes, Susquehanna Shale Hills Critical Zone Observatory, Providence Creek Headwater Catchments (1660 - 2115 m elevation), Wolverton Basin (2230 - 2700 m elevation), Other instrumented sites • Climatology / Meteorology, Hydrology, Soil Science / Pedology • Boulder Creek Critical Zone Observatory; Catalina-Jemez Critical Zone Observatory; Luquillo Critical Zone Observatory; Shale Hills Critical Zone Observatory; Southern Sierra Critical Zone Observatory; Christina River Basin Critical Zone ObservatoryNational - Stream Water Chemistry - Cations, Anions, Metals (1982-2015)
1 components • Bisley, Betasso, East Peak, Marshall Gulch (High-Elevation), Providence Creek Subcatchment P301, Providence Creek Subcatchment P303, Providence Creek Subcatchment P304, Eel River Watershed, Puente Roto, Rio Blanco, Rio Icacos, Susquehanna Shale Hills Critical Zone Observatory • Biogeochemistry, Biology / Ecology, Hydrology, Water Chemistry • Hyojin, Kim; Bishop, Jim; Dietrich, William; Fung, Inez; McDowell, William H.; Brantley, Susan L.; Hoagland, Beth; Sullivan, Pamela L.; Cain, Molly; Neal, Andrew; Fisher, Jessica; Russo, Tess; Niwot Ridge LTER; Liu, Fengjing; Chorover, Jon; Troch, Peter; McIntosh, Jennifer; Brooks, Paul; Abramson, Nate; Heidbuechel, Ingo; Amistadi, Mary Key; Alexander Pedron, Shawn; Chorover, Jon; Troch, Peter; Corley, Timothy; Zapata-Rios, Xavier; Losleben, Mark; Condon, Katherine -
Partner Organizations
-
Topography
0 - 1043 m elevation (268 m mean)
The headwaters of granodioritic Río Blanco are unusually flat before cascading
steeply down the side of the batholith and leveling out along the alluvial coastal plain. The inflection point where the stream sharply steepens occurs at the edge of
a non-glacial hanging valley. -
Human Impacts
- forest land
- urban or built-up land
Headwaters are within El Yunque National Forest, while the coastal plain has urban areas and major roads.
Explore Further








