Pelletier et al., 2018
Which way do you lean? Using slope aspect variations to understand Critical Zone processes and feedbacks.
Pelletier J. D., Barron‐Gafford G. A., Gutiérrez‐Jurado H., Hinckley E.‐L. S., Istanbulluoglu E., McGuire L. A., Niu G.‐Y., Poulos M. J., Rasmussen C., Richardson P., Swetnam T. L., and Tucker G. E. (2018)
Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 43(5): 1133–1154 Cross-CZO
-
Catalina-Jemez, INVESTIGATOR
-
Catalina-Jemez, INVESTIGATOR
-
Boulder, INVESTIGATOR
-
Catalina-Jemez, INVESTIGATOR, COLLABORATOR
-
Catalina-Jemez, INVESTIGATOR
-
Catalina-Jemez, INVESTIGATOR
-
Boulder, INVESTIGATOR
Abstract
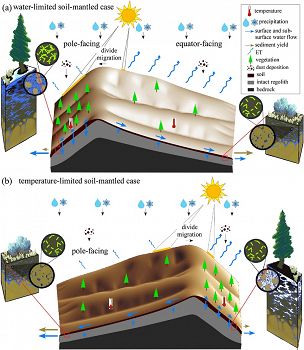
Conceptual models for (A) water‐limited and (B) temperature‐limited soil‐mantled cases. Blue represents water in soil pore spaces while white represents air. In (A), soils are poorly developed on equator‐facing hillslopes, limiting water storage potential. In (B), soils are more well developed on equator‐facing hillslopes but higher PET results in lower water storage.
Soil‐mantled pole‐facing hillslopes on Earth tend to be steeper, wetter, and have more vegetation cover compared with adjacent equator‐facing hillslopes. These and other slope aspect controls are often the consequence of feedbacks among hydrologic, ecologic, pedogenic, and geomorphic processes triggered by spatial variations in mean annual insolation. In this paper we review the state of knowledge on slope aspect controls of Critical Zone (CZ) processes using the latitudinal and elevational dependence of topographic asymmetry as a motivating observation. At relatively low latitudes and elevations, pole‐facing hillslopes tend to be steeper. At higher latitudes and elevations this pattern reverses. We reproduce this pattern using an empirical model based on parsimonious functions of latitude, an aridity index, mean‐annual temperature, and slope gradient. Using this empirical model and the literature as guides, we present a conceptual model for the slope‐aspect‐driven CZ feedbacks that generate asymmetry in water‐limited and temperature‐limited end‐member cases. In this conceptual model the dominant factor driving slope aspect differences at relatively low latitudes and elevations is the difference in mean‐annual soil moisture. The dominant factor at higher latitudes and elevations is temperature limitation on vegetation growth. In water‐limited cases, we propose that higher mean‐annual soil moisture on pole‐facing hillslopes drives higher soil production rates, higher water storage potential, more vegetation cover, faster dust deposition, and lower erosional efficiency in a positive feedback. At higher latitudes and elevations, pole‐facing hillslopes tend to have less vegetation cover, greater erosional efficiency, and gentler slopes, thus reversing the pattern of asymmetry found at lower latitudes and elevations. Our conceptual model emphasizes the linkages among short‐ and long‐timescale processes and across CZ sub‐disciplines; it also points to opportunities to further understand how CZ processes interact. We also demonstrate the importance of paleoclimatic conditions and non‐climatic factors in influencing slope aspect variations.
Citation
Pelletier J. D., Barron‐Gafford G. A., Gutiérrez‐Jurado H., Hinckley E.‐L. S., Istanbulluoglu E., McGuire L. A., Niu G.‐Y., Poulos M. J., Rasmussen C., Richardson P., Swetnam T. L., and Tucker G. E. (2018): Which way do you lean? Using slope aspect variations to understand Critical Zone processes and feedbacks. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 43(5): 1133–1154. DOI: 10.1002/esp.4306
 This Paper/Book acknowledges NSF CZO grant support.
This Paper/Book acknowledges NSF CZO grant support.
Explore Further