Law et al., 2019
Bioclimatic Envelopes for Individual Demographic Events Driven by Extremes: Plant Mortality from Drought and Warming
Law D.J., Adams H.D., Breshears D.D., Cobb N.S., Bradford J.B., Zou C.B., Field J.P., Gardea A.A., Williams A.P., and Huxman T.E. (2019)
International Journal of Plant Sciences 180(1): 53-62
-
Catalina-Jemez, INVESTIGATOR, COLLABORATOR
-
Catalina-Jemez, INVESTIGATOR
-
Catalina-Jemez, INVESTIGATOR
Abstract
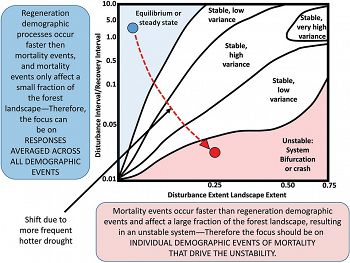
Schematic showing the stability and variability in the proportion of the landscape covered by mature vegetation and the results of a shift from an equilibrium state (blue) to an unstable state (red) due to more frequent and hotter drought. The schematic highlights that demographic processes, including mortality, can be averaged across all demographic events in an equilibrium state (blue box), whereas focusing on individual demographic events such as mortality is appropriate in an unstable state (red box; adapted from Turner et al. 1993)
The occurrence of plant species around the globe is largely constrained by climate. Ecologists use plant-climate relationships such as bioclimatic envelopes to determine environmental conditions that promote probable species occurrence. Traditional bioclimatic envelopes exclude disturbance or only include disturbance as infrequent and small-scale effects, assuming that the net effect of climate on demographic processes predicts longer-term equilibrial responses of biota. Because of the increasing frequency and extent of extreme events associated with climate change, ecologists may need to increase focus on individual demographic events driven by extreme events such as large-scale tree die-off. Approaches that predict traditional equilibrial biogeographic responses associated with long-term trends in mean climate could be complemented with an expanded focus on how extreme events catalyze individual demographic events. Extreme conditions of drought are often a prerequisite for abrupt demographic events such as large-scale tree die-off, with the effects of extremes often exacerbated by climatic trends such as warming. In this Perspective, we illustrate the use of bioclimatic envelopes for predicting individual demographic events. Currently, data on conditions that drive individual demographic events are usually aggregated across time and/or are correlative. We highlight this approach with a case study of experimentally drought-induced mortality in Pinus edulis trees, resulting from a combination of ecologically extreme conditions in one parameter and a shifting distribution in another: drought under higher temperatures. Based on this example, we predict a more than fivefold increase in the frequency of die-off events under a global change scenario of high emissions. This general approach complements traditional bioclimatic envelopes and more detailed physiological approaches that are currently being refined to address climate change challenges. Notably, this approach could be developed for other climate conditions and plant species and may improve predictions of abrupt demographic events that are altering ecosystems globally.
Citation
Law D.J., Adams H.D., Breshears D.D., Cobb N.S., Bradford J.B., Zou C.B., Field J.P., Gardea A.A., Williams A.P., and Huxman T.E. (2019): Bioclimatic Envelopes for Individual Demographic Events Driven by Extremes: Plant Mortality from Drought and Warming. International Journal of Plant Sciences 180(1): 53-62. DOI: 10.1086/700702
 This Paper/Book acknowledges NSF CZO grant support.
This Paper/Book acknowledges NSF CZO grant support.
Explore Further