Swetnam et al., 2016
Tree Morphologic Plasticity Explains Deviation from Metabolic Scaling Theory in Semi-Arid Conifer Forests, Southwestern USA
Swetnam T.L., O’Connor C.D., Lynch A.M. (2016)
PLoS ONE 11(7): e0157582
-
Catalina-Jemez, INVESTIGATOR
Abstract
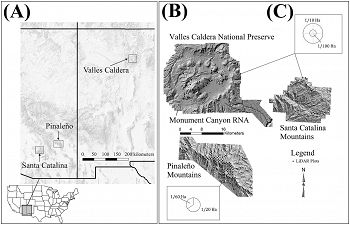
(A) Location of the three study areas, (B) Surface models showing topographic variability and plot location, and (C) sampling plot layouts.
A significant concern about Metabolic Scaling Theory (MST) in real forests relates to consistent differences between the values of power law scaling exponents of tree primary size measures used to estimate mass and those predicted by MST. Here we consider why observed scaling exponents for diameter and height relationships deviate from MST predictions across three semi-arid conifer forests in relation to: (1) tree condition and physical form, (2) the level of inter-tree competition (e.g. open vs closed stand structure), (3) increasing tree age, and (4) differences in site productivity. Scaling exponent values derived from non-linear least-squares regression for trees in excellent condition (n = 381) were above the MST prediction at the 95% confidence level, while the exponent for trees in good condition were no different than MST (n = 926). Trees that were in fair or poor condition, characterized as diseased, leaning, or sparsely crowned had exponent values below MST predictions (n = 2,058), as did recently dead standing trees (n = 375). Exponent value of the mean-tree model that disregarded tree condition (n = 3,740) was consistent with other studies that reject MST scaling. Ostensibly, as stand density and competition increase trees exhibited greater morphological plasticity whereby the majority had characteristically fair or poor growth forms. Fitting by least-squares regression biases the mean-tree model scaling exponent toward values that are below MST idealized predictions. For 368 trees from Arizona with known establishment dates, increasing age had no significant impact on expected scaling. We further suggest height to diameter ratios below MST relate to vertical truncation caused by limitation in plant water availability. Even with environmentally imposed height limitation, proportionality between height and diameter scaling exponents were consistent with the predictions of MST.
Citation
Swetnam T.L., O’Connor C.D., Lynch A.M. (2016): Tree Morphologic Plasticity Explains Deviation from Metabolic Scaling Theory in Semi-Arid Conifer Forests, Southwestern USA. PLoS ONE 11(7): e0157582. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157582
 This Paper/Book acknowledges NSF CZO grant support.
This Paper/Book acknowledges NSF CZO grant support.
Explore Further