MODELS
Researchers at the Susquehanna Shale Hills CZO have developed and implemented a suite of quantitative and qualitative models of critical zone processes. These models characterize the processes that shape the Earth's surface over various time scales. Improving current models and bridging knowledge gaps between different systems are at the core of critical zone research.
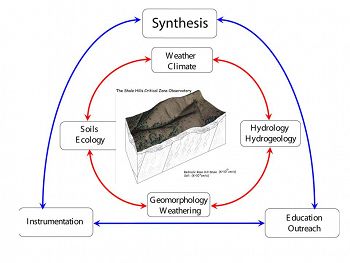
Conceptual Model for Susquehanna Shale Hills CZO
Modelling News

FEATURED
CZ colleagues: Please contact us about proposals for NSF’s CZ Collaborative Network, due 02 Dec 2019
08 Jul 2019 - CZO will end Nov 2020, succeeded by the “CZ Collaborative Network”. Let’s explore how the CZ community can build upon the CZOs via new NSF proposals.

2019 SSHCZO All-Hands Meeting at Penn State
10 May 2019 - The 2019 All-Hands Meeting brought together our core team, our off-campus collaborators, and our outreach partners at Shaver's Creek in a new...

2018 American Geophysical Union Fall Meeting - What Science Stands For
14 Nov 2018 - The Annual Fall Meeting of the American Geophysical Union is a worldwide conference for geophysical sciences, which brings together space scietists,...

Dr. Ying Fan Reinfelder visits for the 2018 All-Hands Meeting at Penn State
10 May 2018 - Over the course of two days each May, the SSHCZO comes together for the annual All-Hands science meeting at Penn State. This year, Dr. Ying...

Delegation from China Geologic Survey visits Shale Hills CZO
03 Nov 2017 - During the week of October 30th, Penn State and SSHCZO hosted 15 scientists from the China Geological Survey, with interests ranging from saltwater...

Water Resources Research Special Collection: Concentration-discharge relations in the critical zone
30 Oct 2017 - Water Resources Research published a new special collection in September 2017 featuring concentration-discharge research from multiple CZOs.
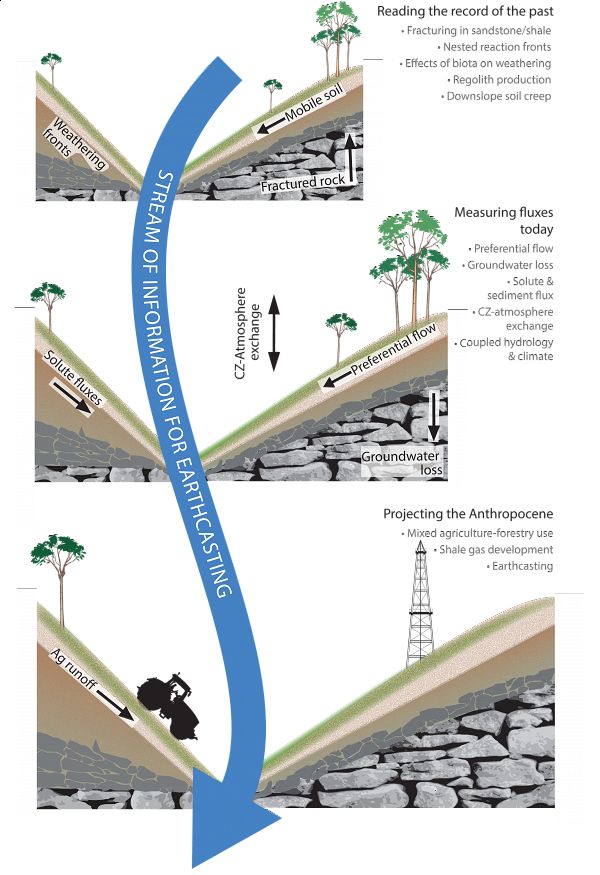
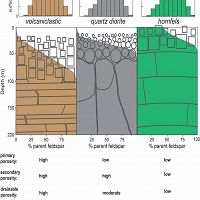
Bedrock-to-Regolith
Bedrock and Regolith Weathering
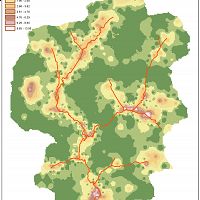
Conceptual models of deep CZ structure and function.
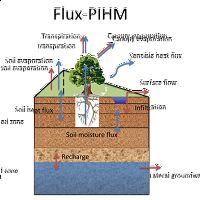
Flux-PIHM
Flux-PIHM
Flux PIHM is a fully-coupled land surface hydrologic model with improved land-atmosphere interactions.
Hydrogeochem
Hydrogeochemical Model
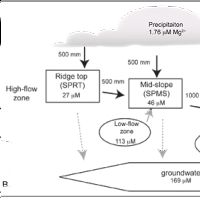
Mass balance model for deposition, weathering and transport at SSHCZO.
Hydropedo Toolbox
Hydropedograph Toolbox
A MATLAB-based toolbox for analysis of time series data for soil moisture profiles
Isotope Weathering
Isotopic Estimates of Weathering
Isotope geochemistry (Uranium, Thorium, Beryllium) offer estimates of weathering rates at Shale Hills.
PIHM
Penn State Integrated Hydrologic Model
Multiprocess, multi-scale hydrologic model.
PIHMGis
GIS interface for Penn State Integrated Hydrologic Model
Tightly coupled GIS interface for the Penn State Integrated Hydrologic Model
PIHMSed
PIHM-Sediment Transport
The 3D landscape evolution model (PIHMSed) that couples the processes of bedrock uplift, weathering, and regolith.
PIHM_DOC
Penn State Integrated Hydrological Model for Dissolved Organic Carbon
PIHM is a physically based, fully distributed hydrological model
Preferential Flow
Hydrologic Flowpaths and Hydropedology
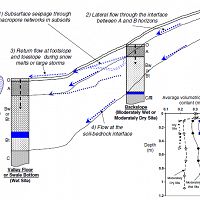
Vertical and lateral flowpaths provide a "short-circuit" for water flux in the shallow subsurface.
Explore Further