Brecheisen et al., 2019
Development and deployment of a field-portable soil O2 and CO2 gas analyzer and sampler
Brecheisen, Zachary S., Charles W. Cook, Paul R. Heine, Junmo Ryang, Daniel deB. Richter (2019)
PLoS ONE 14(8): e0220176
-
Calhoun, GRAD STUDENT
-
Calhoun, STAFF
-
Calhoun, STAFF
-
Calhoun, UNDERGRAD
-
Calhoun, INVESTIGATOR
Abstract
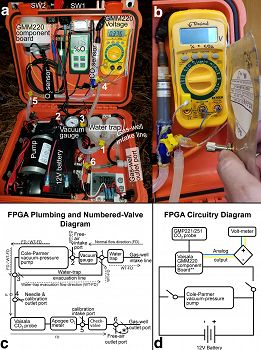
Annotated FPGA components, plumbing, and wiring. a) annotated FPGA components as seen during field deployment, b) closeup view of hypodermic needle filling a gas sample collection bag, c) plumbing diagram of the FPGA indicating flow directions through different components of the FPGA for regular use as well as water-trap evacuation. Numbered 3-way valves with “\” indicating the line is closed during normal use. d) Circuitry wiring diagram for the FPGA.
Here we present novel method development and instruction in the construction and use of Field Portable Gas Analyzers study of belowground aerobic respiration dynamics of deep soil systems. Our Field-Portable Gas Analysis (FPGA) platform has been developed at the Calhoun Critical Zone Observatory (CCZO) for the measurement and monitoring of soil O2 and CO2 in a variety of ecosystems around the world. The FPGA platform presented here is cost-effective, lightweight, compact, and reliable for monitoring dynamic soil gasses in-situ in the field. The FPGA platform integrates off-the-shelf components for non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) CO2 measurement and electro-chemical O2 measurement via flow-through soil gas analyses. More than 2000 soil gas measurements have been made to date using these devices over 4 years of observations. Measurement accuracy of FPGAs is consistently high as validated via conventional bench-top gas chromatography. Further, time series representations of paired CO2 and O2 measurement under hardwood forests at the CCZO demonstrate the ability to observe and track seasonal and climatic patterns belowground with this FPGA platform. Lastly, the ability to analyze the apparent respiratory quotient, the ratio of apparent CO2 accumulation divided by apparent O2 consumption relative to the aboveground atmosphere, indicates a high degree of nuanced analyses are made possible with tools like FPGAs. In sum, the accuracy and reliability of the FPGA platform for soil gas monitoring allows for low-cost temporally extensive and spatially expansive field studies of deep soil respiration.
Citation
Brecheisen, Zachary S., Charles W. Cook, Paul R. Heine, Junmo Ryang, Daniel deB. Richter (2019): Development and deployment of a field-portable soil O2 and CO2 gas analyzer and sampler. PLoS ONE 14(8): e0220176. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220176
 This Paper/Book acknowledges NSF CZO grant support.
This Paper/Book acknowledges NSF CZO grant support.
Explore Further