Numerical Models
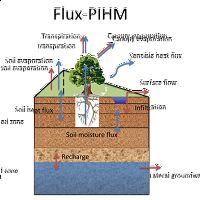
Flux-PIHM
Flux-PIHM
Flux PIHM is a fully-coupled land surface hydrologic model with improved land-atmosphere interactions.
Hydropedo Toolbox
Hydropedograph Toolbox
A MATLAB-based toolbox for analysis of time series data for soil moisture profiles
PIHM
Penn State Integrated Hydrologic Model
Multiprocess, multi-scale hydrologic model.
PIHMGis
GIS interface for Penn State Integrated Hydrologic Model
Tightly coupled GIS interface for the Penn State Integrated Hydrologic Model
PIHMSed
PIHM-Sediment Transport
The 3D landscape evolution model (PIHMSed) that couples the processes of bedrock uplift, weathering, and regolith.
PIHM_DOC
Penn State Integrated Hydrological Model for Dissolved Organic Carbon
PIHM is a physically based, fully distributed hydrological model
Numerical Modeling at Susquehanna Shale Hills CZO
The SSHCZO research group has developed a variety of numerical tools to simulate critical zone processes. These models include simulations of matrix and macropore flow in soils and watershed-scale models for mass and energy transport. Ongoing model development is a core component of research at SSHCZO to produce high-quality simulation and forecast capabilities. Details of the current suite of models are provided here.
Flux PIHM is a fully-coupled land surface hydrologic model.
Flux-PIHM has been implemented at the Shale Hills watershed (0.08 km2) in central Pennsylvania.
Calibration data includes discharge, water table depth, soil moisture content, sensible and latent heat fluxes during the period June and July 2009.
A comparison of hydraulic redistribution occurrence between a north- and a south-facing midslope sites in the Shale Hills CZO in 2010. Shade of vertical lines indicates the number of soil horizons exhibiting diel signals (0 to 5 horizons as indicated by the gray ramp from white to black). It is apparent that the south-facing site had more prevalent hydraulic redistribution, likely due to higher evaporative demand during the growing season.
The next-generation 3D landscape evolution model (PIHMSed) that couples the processes of bedrock uplift, weathering, and regolith transport.
Definition sketch of hillslope
Conversion of mass equation
Explore Further