Catchment-wide model predictions lead to animation of the CZO
17 Jun 2013
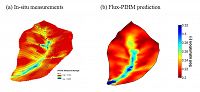
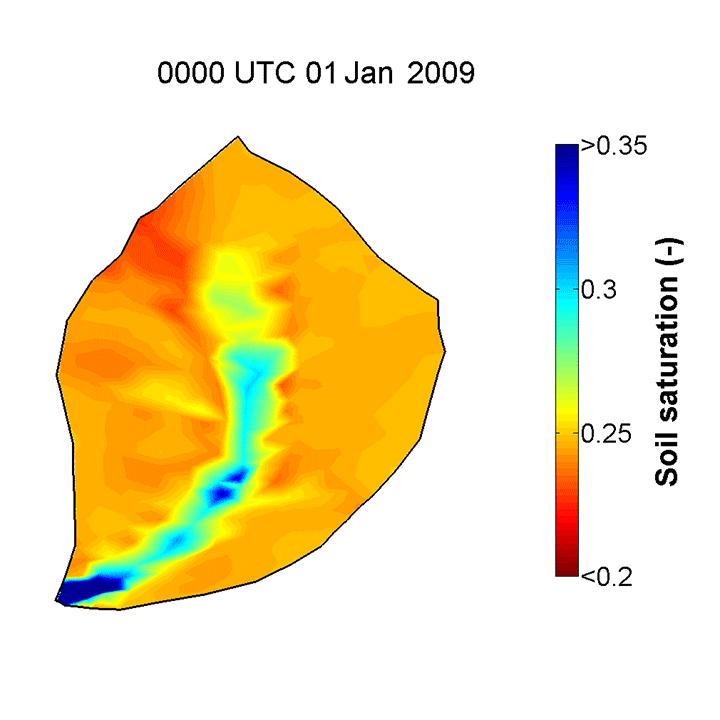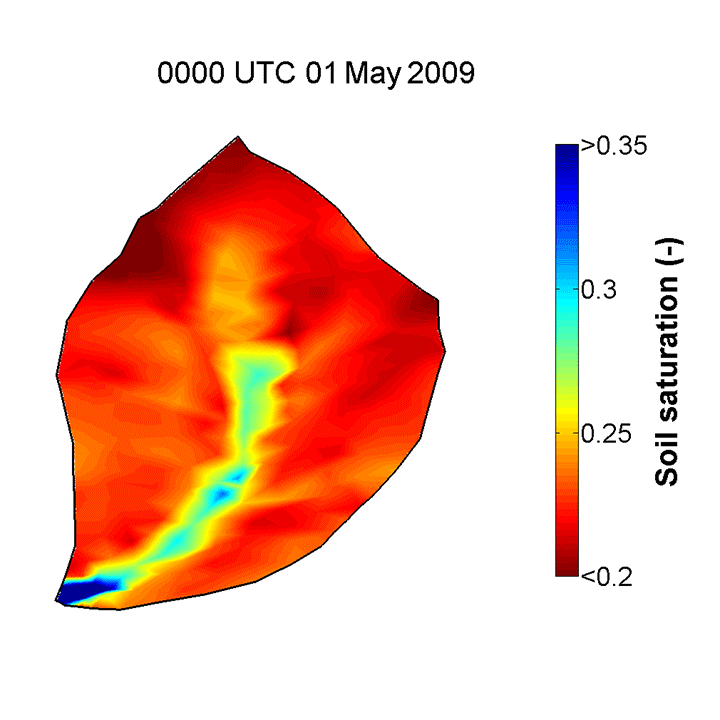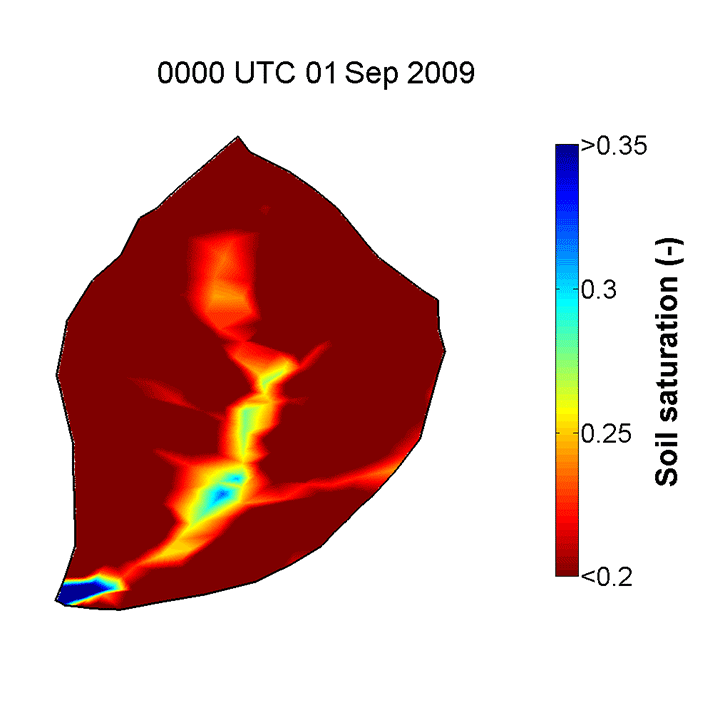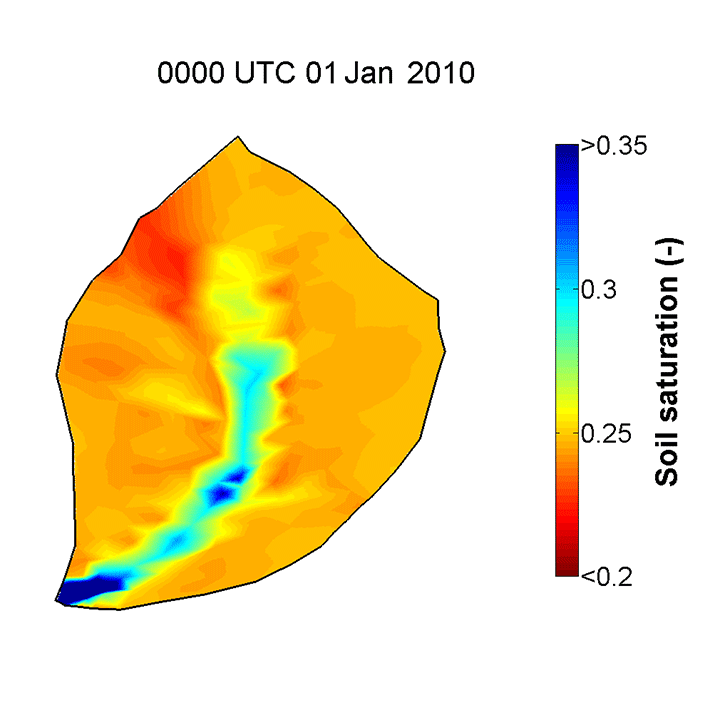
Flux-PIHM, the Penn State Integrated Hydrologic Model which includes a land surface component, is able to provide good predictions of the topographically driven soil moisture pattern observed in the CZO. Yuning Shi, a postdoctoral researcher with the Shale Hills CZO, has demonstrated good agreement in comparisons of in situ soil moisture measurements and Flux-PIHM predicted values. The model resolves the topographically driven effects, predicting wet soil near the stream, dry soil on the hill slope, and relatively wet soil in the swales, just as shown in the observations. The animation below shows the evolution of soil saturation ratio (averaged over the entire soil column) distribution at SSHCZO for the year 2009 as predicted by Flux-PIHM.
News Category:
RESEARCH |
DATA |
MODELS |
EDUCATION/OUTREACH
Publications
2013
Development of a Coupled Land Surface Hydrologic Model and Evaluation at a Critical Zone Observatory. Shi, Y., K. J. Davis, C. J. Duffy, and X. Yu (2013): Journal of Hydrometeorology, 14, 1401—1420
Explore Further